Types of Sensors
You'll be amazed at just how many there are
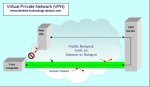
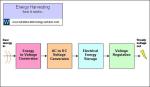
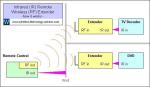
As sensor technology evolves, there are many types of sensors becoming available. More and more sensors will have a wireless function built in. If not, and if required, you can often add it externally... and easily.
So how many sensor types are there?
Well, depending on how you describe them, there are more than 100... and still counting!
Sometimes we describe a sensor by the basic parameter (or variable) that it’s sensing... such as temperature. At other times we may describe it as an air temperature sensor, or a water temperature sensor, or an engine temperature sensor.
It doesn’t really matter. In this case
we are still measuring the same basic parameter - temperature... the
important thing is what we are interested in measuring the temperature
of... what your application is.
There’s no right or wrong way... it’s a
matter of what works... what’s the most convenient... the way that’s
easiest to understand.
Below, you’ll see a list of sensor
types, listed in alphabetical order. The list is a mix of names,
sometimes relating to the basic parameter and sometimes to the
application.
Want more information? Click on those shown as a blue link. These will take you to a page with more detail.
Types of sensors in alphabetical order
- abs sensor
- acceleration - these sensors sense acceleration (a change in velocity) in one, two or three axes (x, y, z) depending on the type.
- acoustic - sense changes in air pressure. This is what our ears sense as sound. An example of an acoustic sensor is a microphone.
- air bag - these use an acceleration sensor as the trigger. If the sensor detects a rapid rate of deceleration, such as a car hitting a brick wall, the air bag is inflated.
- air flow
- air mass
- air quality - there are many pollutants that lower the quality of our air. Gases such as nitrous oxides, carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide and sulphur dioxide; particulates such as Pm10, Pm 5 and PM 2,5 that can enter our lungs, while transporting harmful chemicals or simply reducing lung volume.
- air temperature - for measuring the ambient temperature of the air
- alarm motion
- ambient light
- angle
- aps advanced positioning
- ascender
- automotive oxygen
- automotive
- barometric pressure sensor - for measuring the weight of air pressing down on the earth's surface. Air is most dense at the Earth's surface and decreases in density with increasing altitude, eventually becoming 'vanishingly thin'.
- beam
- bed occupancy
- biometric- these electronically scan and process characteristics such as fingerprints to provide fast authentication to enable entry to buildings, use of machinery etc.
- cam position sensor
- capacitance - the capacity to store electric charge
- capacitive humidity - used to measure the percentage of water vapour in the air
- capacitive proximity - senses when something is getting close by sensing a change in capacitance. This is one of those types of sensors that either gives an output proportional to size of the object approaching and how closely it approaches or switches when it reaches a threshold, for example in a 'non-contact' liquid level sensor..
- car parking
- car
- carbon dioxide (CO2) - for measuring the concentration of carbon dioxide in the air
- ccd
- chair
- chemical - these may present a catalytic surface to the chemical species you want to sense. When that chemical is present, there's a chmical reaction at the surface. This generates an electrical signal that's proportional to the concentration of the chemical.
- carbon monoxide (CO) - carbon monoxide concentration in air
- conductivity - tells us how well a liquid will conduct electricity
- coolant level
- coolant temperature
- crank angle
- crank position
- current (electric)
- displacement sensor - for sensing changes in position
- distance
- door
- dpfe
- driveway motion
- engine knock
- electrical conductivity (EC)
- faucet sensor
- fiber optic
- fingerprint - these will become more popular as a means to verify personal identity
- flame
- flow
- fluxgate magnetic
- force
- frequency - the number of times something happens every second, measured in Hertz (a long time ago this was called cycles per second).
- fuel flow
- fuel level
- garage door sensor
- garage parking
- gas sensor - for measuring the concentration of gases
- glass break
- glucose - senses the concentration of glucose in blood
- gps - global positioning system, senses location on the earth's surface
- gyro
- hall effect sensor - senses a magnetic field
- heat
- home security
- humidity
- inertial sensor
- infrared - for sensing invisible Infrared light
- ir beam
- lambda sensor
- laser
- light
- lightning - detects pulses of the electromagnetic energy generated by discharges. A system of sensors can locate the position of a lightning strike to about a kilometre, though these are usually operated as a service by meteorological organizations. They may even give a value for the electric current (Amperes) that flows and its direction.
- linear position
- liquid level - can sense the position of the liquid surface from above with an ultrasonic sensor, or have a float coupled to an electronic rotary encoder or a pressure sensor that measures the weight of the water above it.
- load - a load cell produces a signal proportional to the weight that's on it.
- magnetic proximity
- magnetic
- map
- mass air flow
- mems - micro electro mechanical systems, include vibration sensors
- microwave motion
- moisture - usually measure the amount of moisture on a surface
- motion -
- movement
- natural gas sensor - concentration of the gas in air
- oil pressure sensor - can provide an indication of oil pump failure or lack of oil to lubricate moving mechanical parts such as pistons.
- oxygen - gaseous (eg. in air) or dissolved oxygen (DO) in water. DO is important to aquatic animals such as fish. Aquatic plants can deplete oxygen from water at night, when they respire, but generate oxygen in sunlight when they photosynthesize.
- parking sensor - a sensor activated by a car in a parking building. Useful for flagging which parking spaces are available and which are taken up.
- pH - the acidity (hydrogen ion concentration)
- photoelectric - light energy is converted to a proportional amount of electric current.
- piezoelectric - senses sound or vibration, producing a voltage
- pir motion - passive InfraRed, where the heat given off by a person or animal is detected by an InfraRed sensor.
- position
- pressure - measures the amount of force,such as weight, bearing down on a surface
- proximity - how close a thing is to something else
- rain - presence, volume and intensity
- reed - a switch that can be activated by a magnet and often used in security applications
- remote - any sensor that's wirelessly linked to the base station.
- rfid - for electronic identification
- smart - this is a term used to describe sensors that have processing power. They can be configured, make decisions and adapt to different situations, such as automatically change range to preserve the best resolution possible.
- soil moisture - for sensing the water content in a volume of soil.
- solar - These sense solar radiation. There are different types, depending on what part of the sun's radiation you want to measure. Some measure direct radiation by 'looking' directly at the sun. Others measure indirect solar radiation, measuring the backscatter or reflection from the atmosphere while shaded from the direct rays. Some measure the full visible spectrum and others measure that part of the visible spectrum that makes plants grow... the part that drives photosynthesis. These are called PAR sensors.
- speed
- strain - for measuring length change due to applied force
- stud
- temperature sensor - for measuring temperature of most things
- tire pressure - this is one of the types of sensors that will likely be fitted to all vehicles with pressurized tires some day. These tire pressure monitoring systems can send real-time tire pressure information to a display in a vehicle and give early warning if the pressure in any tire is outside its normal range.
- torque sensors - for measuring turning force
- touch
- ultrasonic level sensor
- ultrasonic wind
- ultraviolet (uv)
- vacuum sensor
- velocity
- vibration
- water level sensor
- weight
- wheelchair
- wii sensor bar
- window
- wireless driveway
This list of types of sensors is by no means complete and many new sensors, such as those that sense specific chemicals, are already emerging.
Go from Types of Sensors To Wireless Sensors